What Moves Bitcoin’s Price?
Since Bitcoin (BTCUSD) is considered the world’s most popular Cryptocurrency and its effects extend to the overall Crypto market, it may be worth keeping in mind the factors that can affect its prices.
How Does Bitcoin Operate?
Among one of the main factors behind Bitcoin’s price swings is the fact it operate without a central bank to regulate and influence the currency’s valuation. Instead, Bitcoin runs on a decentralized platform where independent miners offer their computing power to continuously maintain the blockchain ledger.
Central banks have various tools such as interest rates and bonds to increase or reduce inflation, crypto currencies such as Ethereum (ETHUSD), and even Bitcoin are valued at the whim of the open market.
Despite these hurdles, Bitcoin maintains its value using a system of protocols, hard forks (radical changes to the blockchain network’s protocol), halving events, and relying on external factors. All of which, Bitcoin CFD traders should take into account before opening a position.
Illustrative prices.
What Influences Bitcoin’s Price?
A plethora of factors can affect Bitcoin’s prices, and just like other cryptocurrencies and market instruments, Bitcoin can experience volatility and can be dependent on many factors. Below, we mention what can influence its prices.
Availability and Competition
Bitcoin is mined by individuals who maintain the system and uphold the most up-to-date protocols. Miners verify the legitimacy of Bitcoin transactions through their own computers. In return, for adding blocks to the system, or approving transactions, they are awarded a certain amount of Bitcoin for each block they process. This reward is cut in half with every 210,000 blocks that are added to the system and are known as ‘halving events’.
In 2009, miners were awarded 50 Bitcoin, in 2013 it was 25, in 2018 it was 12.5, and in 2020, it was reduced to 6.25.
The high cost of mining through equipment, electricity, and maintenance requires the selling of Bitcoin to be worthwhile to the miner. If the value of Bitcoin drops too low, the Miner may either stop mining, or hold on to their Bitcoin until the valuation rises. As demand rises, so too may the valuation of the coin.
ValuationMarketplaces consist of buyers and sellers. Ideally, this will create a balance where the amount someone is willing to pay for something is high enough that the seller is willing to part with their goods.
Having more people wanting to purchase Bitcoin usually will drive up the price. Demand for the coin is also impacted by how many marketplaces, such as PayPal, allow users to use the coin.
Use cases
Unlike Ether, which is intended for use only on specific platforms, Bitcoin was created to be used as an alternative form of currency. This means that it relies on individuals to appreciate its worth by trading or spending it, so its value can keep rising with market demand.
Trader Sentiment
Some people may hold Bitcoin with the intention of using it to make purchases, similar to how we use fiat currencies. Others may purchase Bitcoin with the intention to trade it. Holding on to the coin until the value rises, then exchanging it for Dollars, Euros, or any other currency. The more a currency is exchanged, the higher potential there is for speculation and volatility.
By owning the underlying asset, it requires the owner to hold the coin, pay maintenance fees, and find a buyer when they are ready to sell. As an alternative, some traders trade CFDs as a way of placing leveraged trades where they can open positions to both go long or short on Bitcoin’s valuation.
Forks & Governance
Hard forks, which indicate a major shift in protocol that all network validators must follow, creates the potential for price volatility. There are times that some miners may choose not to switch to the new governing protocols due to a disagreement with them or another reason.
When this happens, all miners who stick to an older protocol are no longer part of the Bitcoin network. Their coins are viewed as a new currency, affecting the availability in the market. This is how Bitcoin Cash ABC (BABUSD) was created.
Crypto Regulations
Bitcoin, like other cryptocurrencies, does not have a central bank to regulate its value. This is a feature that many people like most about blockchain technologies but it also lends itself to unpredictable valuations. Traders should remain aware that as greater use cases are created and adoption of these digital coins become more widespread, there are also opportunities for high volatility along with risks.
Economic Events
Stock market volatility and price swings can have a direct impact on Cryptocurrencies as they can affect the supply and demand chains for Bitcoin.
Global Developments
Global shifts, encompassing news and events spanning from natural occurrences to geopolitical developments, have the capacity to impact Bitcoin prices due to their effect on trader sentiment.
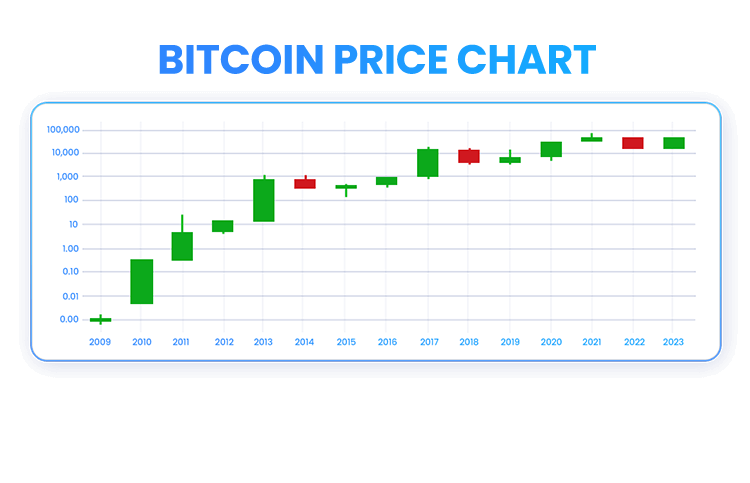
What Were the Highest and Lowest Bitcoin Prices Between 2009 to 2023?
The most expensive Bitcoin price was $67,566.83 on November 8, 2021, and the lowest price was its initial trading price which was $.09 on July, 2010.
Bitcoin’s Price Chart
Here’s a historical price chart depicting Bitcoin’s price swings from 2009 up until 2023.
2009
When it was officially launched on January 3, 2009, Bitcoin, perhaps unsurprisingly, was priced at about zero dollars, or $0.00099. As such, traders using the BitcoinTalk forum traded Bitcoin via PayPal (PYPL) and paid $5.02 per 5,050 Bitcoins.
2010-2013
On October 26, 2010, between was priced at $0.3. One of the most famous Crypto stories that year is perhaps the fact that one Bitcoin owner bought two pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins. This event was deemed the first of its kind as this was the first time someone used a Cryptocurrency to buy real-world products.
In June 2011 Bitcoin exceeded $30 but then deteriorated and ended the year at about $4.70. In 2012, another major event took place as Bitcoin halved for the first time in history, which made Bitcoin more rare and it ended that year at about $13.50.
This strong performance continued until 2013 as more investors were drawn to it and the first Bitcoin ATM emerged in Vancouver, hence enabling the exchange of Bitcoins with fiat money (like the US dollar).
Accordingly, in November 2013, Bitcoin exceeded $1,200 while it ended the year at about $805.
2016–2019
In 2016 its prices reached more than $900, and in 2017, Bitcoin hit $1000. In addition, Bitcoin’s price was volatile in 2018-2019 as trading and prices were boosted as Bitcoin broke above $10,000, and later dropped to about $6,638.84 in the middle of December.
2020
2020, which was famously known for the COVID-19 pandemic and its rattling market response, Bitcoin experienced more volatility as it began the year at $6,965.72 fueled by investor concerns about the global economy in the wake of pandemic-related shutdowns and government policies.
As the year hit its end in December, Bitcoin hit over $29,000, which is a boost of over 400% in value since the start of the year.
2021–2023
Bitcoin started 2021 on a high note as it was priced over $40,000 on January 7, and by mid-April Bitcoin hit record-highs surpassing $60,000 in light of Coinbase’s (COIN) IPO and peaked to a record-high of $68,789 on November 10.
This high was later counteracted by continuous drops in 2022 as Bitcoin dropped below $23,000 on June 13, 2022.
Nonetheless, Bitcoin was able to recoup some of its lows in 2023 as it reached over $41,000 on December 4, 2023, driven by hopes of a Fed rate cut and the possibility of Crypto ETFs.
*Subject to operator availability.
